Influence of the Edge Effect on the Tribological Behavior of textured Si-DLC Films under Oil Lubrication
-
摘要: 引起边缘应力集中的边缘效应是影响边界润滑条件下织构材料摩擦学性能的重要因素之一. 本文中采用激光加工、电化学和机械抛光的方法在不锈钢表面制备了边缘未修形和修形凹坑织构,在此基础上采用溅射/射频化学气相沉积技术沉积了Si-DLC膜,研究了边缘修形对织构化薄膜在油中摩擦学性能的影响. 基于有限元方法分析了加载条件下凹坑织构接触界面的应力分布,考察了修形对边缘效应的影响. 结果表明:边缘修形可大幅降低凹坑织构化薄膜与不锈钢对偶球配副间的摩擦以及对偶的磨损. 织构的摩擦学性能与边缘效应呈正相关关系,边缘修形可使凹坑边缘的最大接触应力降低30%左右,有利于缓和凹坑边缘的刮擦作用从而降低织构材料的摩擦磨损.Abstract: Edge effect causing stress concentration at the texture edges is an important factor affecting the tribological properties of textured materials. By laser ablation, electrochemical and mechanical polishing, a series of normal and edge-profiled dimple textures were prepared on stainless steel substrates. Si-DLC films were deposited on the substrates via sputtering and RF-CVD method to obtain the untextured, the normal and edge-profiled textured Si-DLC films, and the edge-profiling effect on the tribological performance under oil lubrication of the textured Si-DLC films was investigated. The contact stress distribution of the textures was analyzed by the finite element method to discuss the changes in edge effect due to edge-profiling. The results show that by edge-profiling, the friction of the textured Si-DLC films and the wear of the mated balls, as well as the maximum contact stress concentrated at the edge of the textures were reduced markedly. The tribological properties of the textures were positively related to the edge effect. The reduction of the maximum stress was thought to play an important role in lowering the friction and wear.
-
Keywords:
- textures /
- Si-DLC film /
- edge-profiling /
- stress concentration /
- oil lubrication
-
表面工程技术对改善材料的摩擦学性能、延长机械系统的使用寿命、提高机械效率和承载能力具有重要的促进作用[1],也是降低能源消耗和保护环境的迫切需求[2]. 近年来的研究表明,低副接触配副在润滑状态下凹坑织构可显著降低摩擦系数并提高摩擦副的承载能力而备受关注[3–7]. 比如Wos等[3]的研究结果显示,在较广的温度范围内凹坑织构对多种油润滑状态下的摩擦均具有显著的降低和稳定作用,这种作用在低载和较高温度下更为明显,摩擦系数的最大降幅可达60%以上. 表面织构的降摩减磨机理归因于织构凹坑储存润滑剂和收集磨屑功能.
为提高织构表面的抗磨性能,充分发挥织构表面的储油和收集磨屑及降摩减磨作用,人们研究了TiN[8]、TiAlN[9]和类金刚石(DLC)膜[10–12]等织构化硬质薄膜的摩擦学性能. 其中,DLC膜因具有高硬度、高化学稳定性以及各种环境下优异的摩擦学性能[13–16]而备受关注. 适当孔径、较浅的凹坑织构可使DLC膜在合成油中的摩擦系数降低约30%[12]. 凹坑织构化也使油润滑条件下掺硅DLC(Si-DLC)膜在室温至200 ℃范围内的摩擦系数降低10%~30%,对提高薄膜抗磨性能的作用更为显著,可使薄膜的磨损率降低70%~80%[11]. 织构化对提高润滑状态下DLC膜的抗剥落能力也有积极作用[10].
然而,在低速[4, 11, 17]、高载[3–4]条件下或低黏度油润滑环境中[3–4, 17],织构化对材料的降摩效果较为有限,特别在高副接触下会大幅增加对偶的磨损[17]. 在凹坑孔径和深度尺寸较大时织构化DLC膜的摩擦磨损均远高于无织构薄膜[12]. 一般认为[7, 17],这是由于织构边缘较为尖锐,织构材料与对偶发生直接接触时往往存在引起织构边缘应力集中的边缘效应以及接触界面间的刮擦效应,这使织构配副的摩擦增高且波动增大,对偶的磨损也随之显著增高. Ovaert等[7]的计算结果显示,尖锐的涂层织构边缘存在应力集中尖峰,而圆滑的涂层织构边缘则无应力尖峰. 同时,应力集中程度的增加容易引起织构化DLC膜在边缘处的局部剥落,造成润滑失效,使薄膜的使用寿命和润滑效果受到极大限制. 然而针对织构化材料边缘效应的研究鲜有报道.
边缘效应也是影响滚子轴承寿命的关键问题之一,对滚子边缘进行对数等圆滑曲线修形处理则可大幅缓和边缘效应,从而提高轴承的运行可靠性和使用寿命[18]. 本文作者借鉴滚子轴承中的边缘修形方法,采用激光加工、电化学抛光及机械抛光方法,在不锈钢基体上制备了边缘未修形和边缘修形的凹坑织构,在此基础上制备了摩擦学性能和抗剥落性能[19]较为优异的织构化Si-DLC膜,研究了油润滑条件下织构化Si-DLC膜的摩擦磨损特性,基于有限元法分析了接触状态下凹坑织构化Si-DLC膜与不锈钢球对偶间的接触应力分布,考察了边缘效应对织构化Si-DLC膜在油润滑条件下摩擦学性能的影响. 为了比较,也制备了无织构Si-DLC膜.
1. 试验部分
1.1 织构样品加工
表面织构的加工方法如图1所示. 本文中选用直径40 mm的镜面抛光4Cr13不锈钢盘为无织构基体,采用JT-FB30A激光打标机在无织构基体表面加工了凹坑织构,用2 000#砂纸机械抛光以去除凹坑边缘的堆积物后得到边缘未修形织构基体. 进一步对未修形织构基体依次进行电化学抛光和湿法氧化铝(0.5 μm)机械抛光以去除凹坑边缘的毛刺和边角,得到凹坑边缘呈圆滑过渡的边缘修形织构基体. 电化学抛光条件为温度90 ℃,电流2.3 A,电解时间3 min. 本文中制备的边缘未修形和修形织构凹坑参数为固定凹坑面积密度为10%时凹坑直径分别为50、70和100 μm,固定直径为70 μm的情况下面积密度分别为5%、10%和15%.
1.2 Si-DLC膜的沉积
采用溅射/RF-CVD复合镀膜机,在无织构、边缘未修形和修形织构基体以及单晶硅片表面沉积了引入梯度过渡层的Si-DLC膜[19]. 所用靶材为高纯钛(Ti,质量分数99.9%),溅射气体为氩气(Ar),反应性气体为六甲基二硅氧烷(HMDS),碳源气体为甲苯和HMDS.
沉积薄膜时,首先在氩气流量20 SCCM、射频功率100 W的条件下利用氩离子清洗基体表面15 min,然后依次采用RF-CVD辅助溅射法沉积纯Ti层和梯度过渡层,在溅射功率为100 W,氩气流量15 SCCM的条件下沉积15 min后得到纯Ti层. 继而逐步导入2、3、4和5 SCCM的HMDS,同时调低氩气流量至13、12、11和10 SCCM,使氩气和HMDS总流量保持15 SCCM,在各步条件下分别沉积5 min获得梯度过渡层. 最后,停止Ti靶溅射与氩气导入,利用RF-CVD法,在HMDS和甲苯气体流量分别为5和10 SCCM时沉积60 min得到Si-DLC表层. 从纯Ti层到Si-DLC表层的沉积过程中始终保持施加在基体上的射频功率约为60 W.
对沉积在单晶硅基体上的薄膜,用场发射扫描电镜(SEM)观测了薄膜断面、测量了薄膜厚度,用共焦显微拉曼光谱仪分析表征了薄膜的结构. 如图2所示,所得薄膜均匀致密,结构与文献[19]报道一致.
1.3 摩擦学性能评价与有限元分析
采用球盘式往复摩擦试验机,室温条件下对无织构、边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜进行了油中摩擦学性能的评价. 所用润滑油为150BS基础油,采用将适量润滑油滴加在摩擦配副接触区域、保持摩擦过程中接触界面始终被油所覆盖的润滑方式. 对偶为直径12.7 mm的316L不锈钢球,往复频率为2 Hz,往复振幅为10 mm,载荷为20 N,摩擦时间为120 min. 所有薄膜均做两次摩擦试验,以计算薄膜的平均摩擦系数和对偶球的比磨损率.
摩擦试验结束后,用光学显微镜观察了薄膜和对偶球的磨痕,用白光干涉仪对磨痕内织构边缘轮廓进行了测量,假定对偶球磨痕为平面的情况下计算了对偶球的比磨损率,并基于有限元方法和测得的凹坑边缘轮廓与对偶球磨痕,分析了稳定摩擦阶段接触区域的静态接触应力分布.
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 摩擦学性能
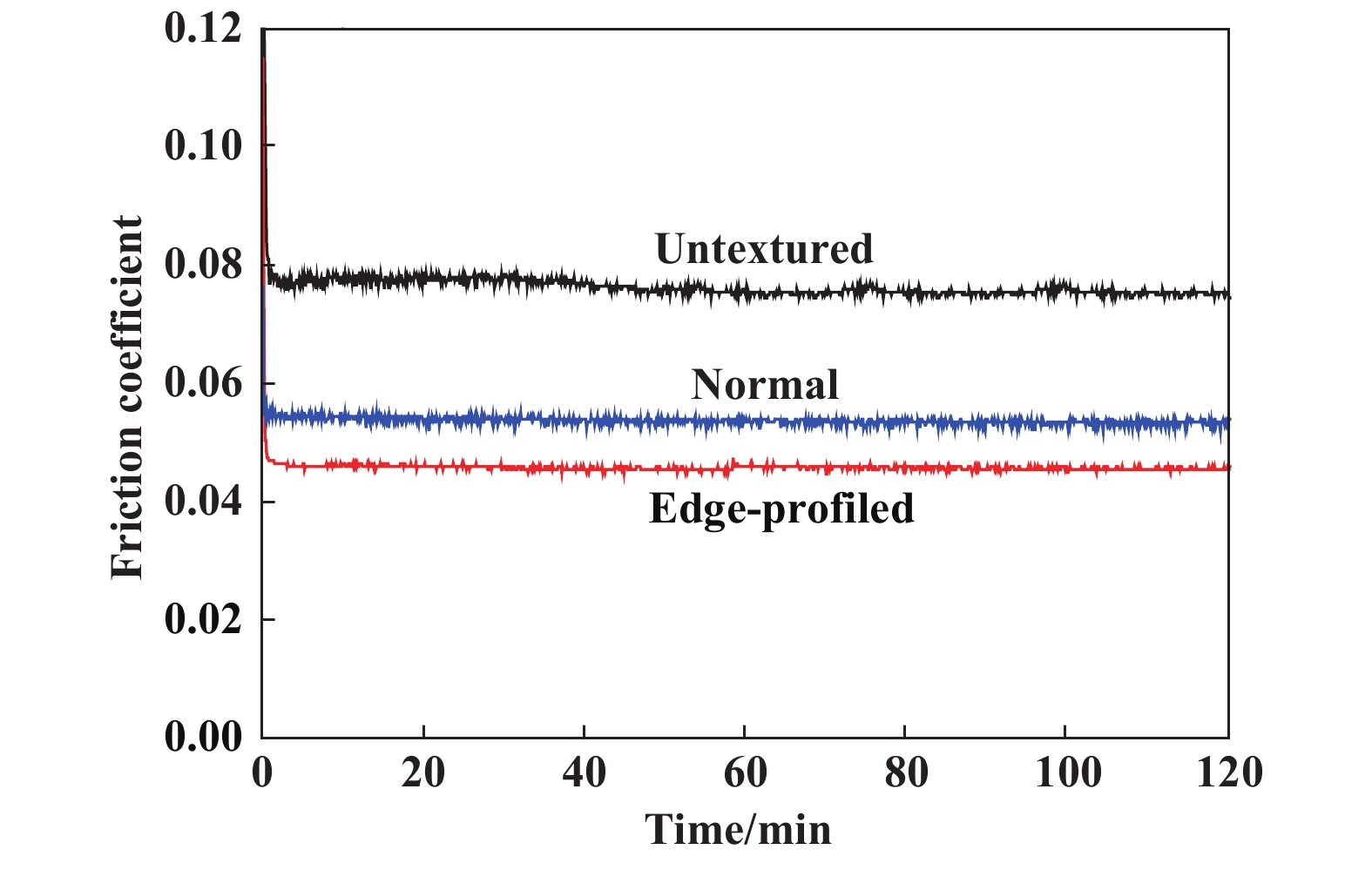
图3给出了无织构(Untextured)、凹坑直径70 μm、面积密度10%边缘未修形(Normal)和修形(Edge-profiled)织构化Si-DLC膜的摩擦曲线. 可见,所有薄膜的摩擦系数在初始阶段均快速下降,然后趋于稳定. 在稳定摩擦阶段,无织构Si-DLC膜的摩擦系数最高,为0.075. 边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜的摩擦系数分别为0.054和0.045,均呈现出低且稳定的摩擦曲线. 与无织构薄膜相比,边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜的摩擦系数分别降低了约28%和40%,织构化可大幅降低并稳定Si-DLC膜在油润滑条件下的摩擦. 边缘修形对织构化薄膜摩擦的降低效果更为显著. 其他各种织构化Si-DLC膜的摩擦曲线与之类似.
取两次摩擦试验中后半60 min区间的所有摩擦系数值计算了无织构(Diameter 0 μm或Density 100%)与织构化Si-DLC膜的平均摩擦系数,如图4所示. 误差条表示所有摩擦系数的波动范围. 所有边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜的平均摩擦系数均低于无织构Si-DLC膜的摩擦系数. 凹坑密度为10%时,凹坑直径70 μm的织构化薄膜具有最低的摩擦系数. 凹坑直径为70 μm时,增大或减小凹坑密度均不利于降低薄膜的摩擦. 对比各种织构化Si-DLC膜,凹坑直径70 μm、密度10%的修形织构化薄膜具有最低的摩擦系数以及更显著的降摩效果.
摩擦试验后用光学显微镜对薄膜及对偶磨痕进行了观察,所有薄膜均未出现局部剥落现象. 图5示出了凹坑直径70 μm、密度10%的边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜及其对偶球磨痕的光学显微照片,作为比较,也给出了无织构薄膜与对偶球磨痕的照片. 无织构Si-DLC膜的磨损划痕较为明显,边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜的表面均只有较浅的划痕,特别是修形织构化薄膜表面的划痕最少. 从所有薄膜对偶表面未观察到明显的转移物存在. 与无织构薄膜配副的对偶球磨痕最大,半径约为380 μm,发生了严重的梨沟磨损. 未修形织构化薄膜对偶球的磨痕显著小于无织构薄膜的对偶,半径约为200 μm. 修形织构化薄膜的对偶球则显示出最小的磨痕半径155 μm,磨损程度最低. 显然,凹坑织构化,特别是边缘修形凹坑织构化可显著提高Si-DLC膜及其对偶球的抗磨损性能.
利用磨痕直径计算了对偶球的比磨损率,如图6所示. 无织构Si-DLC膜对偶球的比磨损率为32×10–8 mm3/(N·m),所有织构化薄膜对偶球的磨损均显著低于无织构薄膜对偶球的磨损. 与未修形织构化薄膜相比,边缘修形织构化薄膜对偶球的磨损得到了大幅降低. 与摩擦特性相一致,凹坑直径70 μm、密度10%的边缘修形织构化薄膜显示出最优的对对偶球的减磨性能,对偶球的比磨损率仅为2×10–8 mm3/(N·m)左右. 减小或增大凹坑直径和密度均会不同程度地增加对偶球的磨损. 减小直径或密度会使织构化的效果减弱,增大直径或密度时则会使接触面积减小、接触应力尖峰增大,导致织构边缘处刮擦效应以及摩擦磨损的增加[7].
2.2 表面织构的应力分析
修形在降摩减磨中所起的作用主要源于边缘效应的减弱即织构边缘接触应力集中程度的降低. 本文中针对摩擦磨损性能较为优异的边缘修形织构化薄膜配副,基于实测的、可拟合为一个对数函数的修形边缘轮廓(如图7中左图)和对偶球的磨痕直径,假定磨痕为平面,建立了对偶球与一个修形凹坑织构接触时的三维模型(如图7中右图,深度50 μm). 针对凹坑直径70 μm、密度10%的未修形织构,设定凹坑织构边缘呈直角的情况下建立了未修形织构的接触模型. 设置材料为结构钢,密度均为7.85 g/cm3,泊松比均为0.3[20–21],对偶球的弹性模量为220 GPa[20],织构材料的弹性模量为230 GPa[21],在载荷20 N的条件下使用ANSYS对模型进行了静态应力分析.
延凹坑中心路径上的接触应力分布曲线如图8所示. 由图8可以看出,织构化薄膜接触面的最大应力均出现在织构边缘附近,凹坑直径70 μm、密度10%的未修形织构边缘出现了一个应力集中尖峰,最大应力达1 185 MPa,而经过修形后应力集中尖峰消失、应力变化较缓和,且最大接触应力降至804 MPa,比未修形织构降低约30%. 可见,边缘修形可大幅减弱织构材料的边缘效应,这将显著降低滑动过程中凹坑边缘处的刮擦效应,从而降低滑动配副的摩擦磨损.
当凹坑直径为70 μm时,凹坑密度5、10和15%边缘修形织构的最大接触应力分别为827、804和859 MPa. 当凹坑密度为10%时,直径50、70和100 μm边缘修形织构的最大接触应力分别为811、804和862 MPa. 最大接触应力的变化趋势与摩擦系数(图4)和对偶球比磨损率(图6)的一致,摩擦磨损特性对边缘效应表现为正相关关系. 边缘效应的减弱以及修形织构边缘与对偶间形成的楔形接触(图7中右图),有利于任意滑动方向上凹坑内的润滑油向接触界面间输送,提高润滑效果. 另外,采用白光干涉仪对修形织构边缘轮廓进行的观察中发现,边缘修形程度与凹坑直径和密度有一定的相关性,这主要受到电化学抛光时凹坑边缘电流密度以及机械抛光时塌边效应不同的影响.
3. 结论
为研究在油润滑条件下边缘效应对织构化Si-DLC膜摩擦学性能的影响,本文制备了无织构以及多种边缘未修形和修形织构化Si-DLC膜. 通过摩擦试验和仿真,评价了Si-DLC膜的摩擦学性能,分析了织构表面静态接触应力分布. 结论如下:
a. 边缘修形可大幅降低织构化Si-DLC膜与不锈钢对偶球配副的摩擦与磨损,其中直径为70 μm、密度为10%的边缘修形织构化Si-DLC膜具有最低的摩擦与磨损,摩擦系数比无织构Si-DLC膜降低40%,比未修形织构化Si-DLC膜降低16%.
b. 对凹坑织构进行边缘修形,可显著减弱边缘效应,使接触条件下织构边缘的应力尖峰消失、应力集中程度更为缓和并有效降低凹坑边缘的最大接触应力. 织构薄膜的摩擦磨损特性与织构边缘的最大接触应力呈正相关关系,削弱边缘效应可使凹坑边缘刮擦效应的作用减弱,从而得到更好的降摩减磨效果.
-
-
[1] Erdemir A. Review of engineered tribological interfaces for improved boundary lubrication [J]. Tribology International, 2005, 38: 249–256 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2004.08.008
[2] Holmberg K, Kivikytö-Reponen P, Härkisaari P, et al. Global energy consumption due to friction and wear in the mining industry [J]. Tribology International, 2017, 115: 116–139 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2017.05.010
[3] Wos S, Koszela W, Pawlus P, et al. Effects of surface texturing and kind of lubricant on the coefficient of friction at ambient and elevated temperatures[J]. Tribology International, 2017, 117: 174–179
[4] 程香平, 康林萍, 张友亮, 等. 润滑条件下菱形孔织构端面摩擦学特性研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2015, 35 (6): 658–664 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2015.06.002 Cheng X, Kang L, Zhang Y, et al. Tribological characteristics of end faces with diamond macro-pores textured under lubrication[J]. Tribology, 2015, 35(6): 658–664 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2015.06.002
[5] Lu H, Ren S, Guo J, et al. Laser textured Co-Cr-Mo alloy stored chitosan/poly (ethylene glycol) composite applied on artificial joints lubrication[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C Materials for Biological Applications, 2017, 78: 239–245
[6] Saeidi F, Parlinska-Wojtan M, Hoffmann P, et al. Effects of laser surface texturing on the wear and failure mechanism of grey cast iron reciprocating against steel under starved lubrication conditions[J]. Wear, 2017, s386–387: 29–38
[7] Ramachandra S, Ovaert T C. Effect of coating geometry on contact stresses in two-dimensional discontinuous films[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2000, 122(4): 665–671 doi: 10.1115/1.1310333
[8] 剡珍, 孙嘉奕, 姜栋, 等. 激光织构化TiN薄膜的干摩擦性能研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2017, 37 (4): 518–526 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.014 Zhen Y, Sun J, Dong J, et al. Tribological behavior of laser textured TiN films under dry friction condition[J]. Tribology, 2017, 37 (4): 518–526 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.014
[9] Sedlaček M, Podgornik B, Ramalho A, et al. Influence of geometry and the sequence of surface texturing process on tribological properties [J]. Tribology International, 2017, 115: 268–273 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2017.06.001
[10] Ding Q, Wang L, Wang Y, et al. Improved tribological behavior of DLC films under water lubrication by surface texturing [J]. Tribology Letters, 2011, 41(2): 439–449 doi: 10.1007/s11249-010-9730-1
[11] Amanov A, Watabe T, Tsuboi R, et al. Improvement in the tribological characteristics of Si-DLC film by laser surface texturing at elevated temperatures[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 232 (10): 549–560
[12] Arslan A, Masjuki H H, Varman M, et al. Effects of texture diameter and depth on the tribological performance of DLC coating under lubricated sliding condition[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 1135–1149 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.194
[13] Kosarieh S, Morina A, Flemming J, et al. Wear mechanisms of hydrogenated DLC in oils containing MoDTC [J]. Tribology Letters, 2016, 64(1): 4–8 doi: 10.1007/s11249-016-0737-0
[14] 张仁辉, 鲁志斌, 王立平. 载荷对氟硅共掺杂类金刚石膜摩擦学性能的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2016, 36 (1): 84–91 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2016.01.013 Zhang R, Zhibin L U, Wang L. Effect on the tribological properties of F and Si codoped diamond-like carbon film [J]. Tribology, 2016, 36 (1): 84–91 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2016.01.013
[15] 谢明玲, 杨皎, 张广安, 等. Si-DLC薄膜在硝酸介质中的腐蚀磨损行为与机理[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2017, 37 (4): 510–517 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.013 Xie M, Yang J, Zhang G, et al. Corrosion-wear mechanism of Si-DLC films in nitric acid solution [J]. Tribology, 2017, 37 (4): 510–517 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.013
[16] 吴行阳, 陈腾, 葛宙, 等. 不同湿度条件下N、Si共掺杂DLC膜的摩擦学性能研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2017, 37(4): 501–509 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.012 Chen T, Wu X, Ge Z, et al. Achieving low friction and wear under various humidity conditions by co-doping nitrogen and silicon into diamond-like carbon films [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2017, 37 (4): 501–509 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2017.04.012
[17] Kovalchenko A, Ajayi O, Erdemir A, et al. Friction and wear behavior of laser textured surface under lubricated initial point contact [J]. Wear, 2011, 271: 1719–1725 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2010.12.049
[18] Oswald F B, Zaretsky E V, Poplawski J V. Effect of roller geometry on roller bearing load-life relation [J]. Tribology Transaction, 2014, 57: 928–938 doi: 10.1080/10402004.2014.927545
[19] 吴行阳, 邓兆星, 黄一鸣, 等. 基于多功率源梯度过渡层的Si-DLC的制备及水润滑性能研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2014, 34 (6): 684–688 doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2014.06.012 Wu X, Deng Z, Huang Y, et al. Preparation and tribological properties in water of Si-DLC film with gradient interlayer deposited by multi-power source technology [J]. Tribology, 2014, 34(6): 684–688 (in Chinese) doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2014.06.012
[20] Oshkour A A, Osman N A A, Bayat M, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analyses of functionally graded femoral prostheses with different geometrical configurations [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 56: 998–1008
[21] Wang X, Yamaguchi A. Characteristics of hydrostatic bearing/seal parts for water hydraulic pumps and motors. Part 1: Experiment and theory [J]. Tribology International, 2002, 35 (7): 425–433 doi: 10.1016/S0301-679X(02)00023-3
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 袁浩恩,吴继忠,王海军,陈文刚,程家豪,郭思良,周意昊,魏北朝,罗海. 表面织构与DLC涂层复合处理影响材料摩擦特性的研究进展. 功能材料. 2024(02): 2091-2104 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王新宇,张帅拓,刘建,鲁晓龙,隋旭东,郝俊英,刘维民. 表面织构对管道内壁碳基涂层润湿性与摩擦学性能影响. 摩擦学学报. 2021(01): 86-94 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: